The mere mention of the word can often elicit a range of emotions and opinions. Some view them as a necessary evil, while others recognize them as the lifeblood of a functioning society. But what exactly are taxes, and why do we need them? In this article, we will provide a simple and understandable introduction to public taxation and finance.

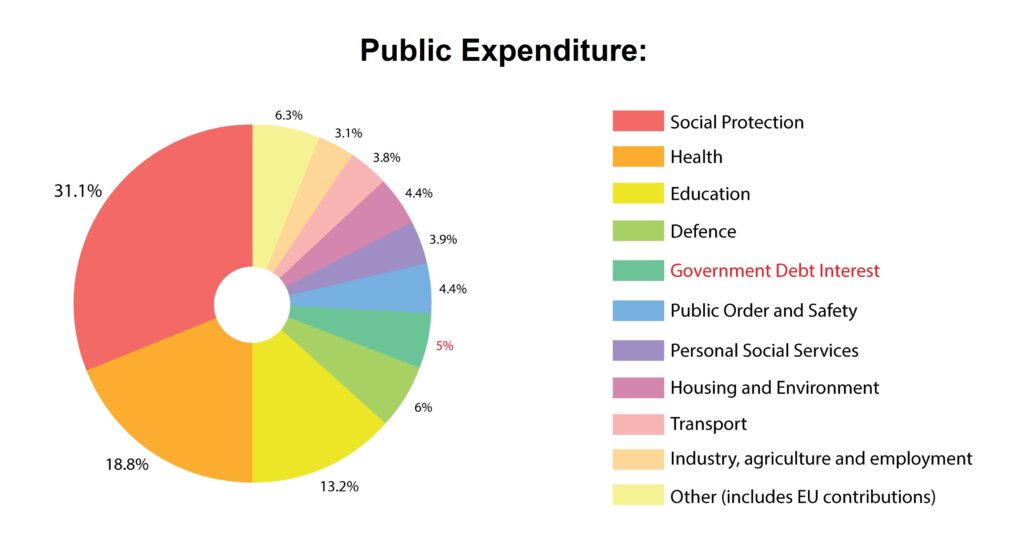
At its core, public taxation is the process through which governments collect funds from individuals and businesses to finance public expenditures. These expenditures encompass a wide range of services and programs that benefit society as a whole, such as infrastructure development, healthcare, education, defense, and social welfare.
Governments rely on taxes to generate revenue, which is then used to cover these public expenses. The funds collected are pooled together and allocated based on the priorities and needs of the society. Without taxation, governments would struggle to provide the necessary infrastructure, services, and public goods that contribute to the overall well-being of citizens.
Now, let’s delve into the key concepts and components of public taxation:
Types of Taxes
Income Tax:
This tax is levied on the earnings of individuals and businesses and is typically calculated based on their income levels.

Sales Tax:
A tax imposed on the purchase of goods and services, usually expressed as a percentage of the transaction value.

Property Tax:
This tax is assessed on the value of real estate properties, including land and buildings.

Corporate Tax:
Imposed on the profits generated by companies.

Excise Tax:
A tax on specific goods like gasoline, tobacco, alcohol, and luxury items.

Customs Duties:
Taxes imposed on imports and exports between countries.

Taxation Process:
Tax Filing:
Individuals and businesses are required to report their income and financial activities to the tax authorities through annual tax returns.
- Tax Assessment: Tax authorities review the submitted returns, ensure compliance, and calculate the tax liability.
- Tax Collection: The tax authorities collect the owed taxes through various methods, such as payroll deductions, direct payments, or withholding at the source.
The Role of Governments:
Public Expenditure: Governments utilize tax revenue to fund public goods, services, and programs that benefit society.
- Economic Stabilization: Taxes can be adjusted to regulate economic conditions, such as managing inflation or stimulating growth.
- Redistribution of Wealth: Progressive tax systems aim to reduce income inequality by imposing higher tax rates on higher income earners and providing social welfare programs to support those in need.
Benefits and Challenges
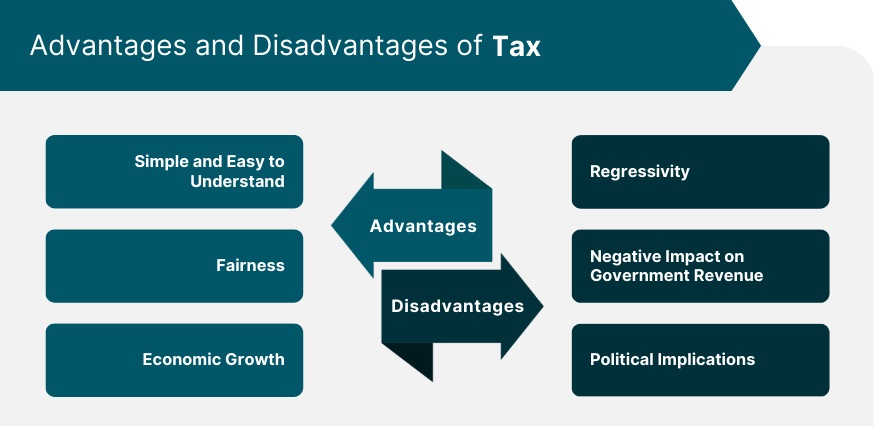
- Benefits: Taxes enable governments to provide essential services and infrastructure, promote economic growth, and support societal well-being.
- Challenges: Balancing tax rates and structures can be complex, as excessive taxation may stifle economic growth, while inadequate taxation may lead to insufficient public funding.
In conclusion, public taxation is the mechanism through which governments finance the provision of public goods and services. While taxes may sometimes seem burdensome, they play a vital role in sustaining and improving our society. Understanding the basics of public taxation empowers individuals to comprehend the broader context in which taxes operate and the benefits they bring to our communities.


alternatives to allergy medication is claritin stronger than benadryl best generic allergy pills
strongest medicine for gerd buy zidovudine medication
purchase isotretinoin sale buy generic absorica isotretinoin online buy
online doctor for sleeping pills generic provigil 100mg
order generic amoxicillin 500mg order amoxil sale amoxicillin 250mg without prescription
order neurontin 800mg sale buy neurontin pills
azipro where to buy buy azithromycin no prescription azithromycin generic
lasix 100mg canada furosemide 100mg brand
buy prednisolone without a prescription order prednisolone 5mg online buy prednisolone 20mg
order amoxil 500mg generic amoxicillin tablet buy amoxicillin 500mg generic
buy generic monodox purchase doxycycline for sale
Greetings from California! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I love the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how quick your blog loaded on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, awesome site!
buy asthma pills oral albuterol buy albuterol 4mg
order amoxiclav pill buy augmentin 1000mg
order generic synthroid 150mcg generic synthroid 150mcg levothyroxine online order
oral levitra 10mg buy levitra cheap
clomid over the counter buy generic clomiphene over the counter buy clomiphene generic
zanaflex cost zanaflex price oral zanaflex
order semaglutide 14mg generic where to buy rybelsus without a prescription rybelsus 14 mg ca
prednisone 20mg drug buy prednisone 5mg online order deltasone 40mg generic
semaglutide pills buy semaglutide 14 mg generic purchase semaglutide online
purchase isotretinoin pill accutane 10mg over the counter isotretinoin 10mg canada
ventolin online ventolin 4mg without prescription albuterol 4mg usa
buy amoxil 250mg generic order amoxil 250mg oral amoxicillin 250mg
oral clavulanate augmentin cheap augmentin 1000mg over the counter
buy zithromax 500mg pills azithromycin 500mg generic azithromycin 500mg tablet
synthroid 150mcg cheap synthroid price levothroid us
omnacortil 20mg price omnacortil 20mg for sale prednisolone 20mg for sale
clomiphene 100mg ca generic serophene order clomiphene online
gabapentin 800mg usa order neurontin 800mg without prescription cheap generic neurontin
viagra next day delivery usa cheap viagra 50mg sildenafil 50mg us
order furosemide without prescription purchase lasix online cheap order furosemide 100mg pill
cheap vibra-tabs vibra-tabs medication monodox online buy
vardenafil 10mg drug levitra 20mg generic levitra 10mg over the counter
casinos casino online usa casino online games for real money
plaquenil for sale online hydroxychloroquine 200mg cost order generic plaquenil 200mg
pregabalin 150mg generic pregabalin over the counter buy lyrica generic
cialis 10mg over the counter cialis 20mg ca generic tadalafil 40mg
order aristocort 10mg pill triamcinolone 4mg drug buy triamcinolone 10mg generic
buy clarinex online cheap cheap desloratadine 5mg buy generic desloratadine 5mg
buy cenforce 100mg generic order cenforce 100mg online cenforce online
aralen 250mg ca buy chloroquine generic chloroquine for sale online
loratadine price loratadine sale oral loratadine 10mg
order lipitor 20mg sale atorvastatin online buy buy atorvastatin 10mg
norvasc buy online order amlodipine 10mg pill buy norvasc 10mg without prescription
order acyclovir 400mg sale order acyclovir pills order allopurinol 100mg generic
canadian pharcharmy’s generic pharmacy
northwestern pharmacy canada [url=http://canadianphrmacy23.com/]a total noob[/url]
order lisinopril 5mg generic purchase lisinopril online cheap zestril tablet
generic rosuvastatin 20mg rosuvastatin 20mg ca ezetimibe uk
prilosec 10mg uk buy prilosec generic order omeprazole for sale
how to buy domperidone buy motilium no prescription tetracycline 250mg generic
order lopressor 100mg generic buy generic metoprolol for sale order lopressor without prescription
order flexeril sale baclofen 10mg sale order baclofen 25mg pill
buy tenormin atenolol 100mg oral order tenormin 50mg generic
buy depo-medrol without a prescription methylprednisolone buy methylprednisolone pills canada
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.